Porcelain crowns are not simply a dental restoration solution — they are also a powerful tool for recreating a radiant, white smile and boosting self-confidence. Among the various methods, anatomical crown and clinical crown are two widely applied techniques that many dentists rely on. In the following article, we’ll help you gain a clearer understanding of these two approaches.
What is the anatomical crown?
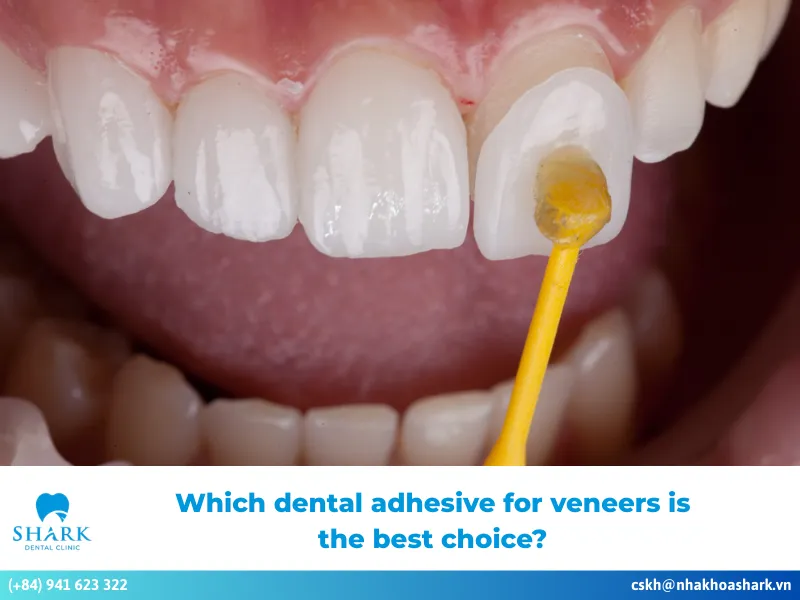
Anatomical crown is a dental procedure that uses a porcelain crown precisely crafted to replicate the natural anatomical shape of a real tooth. This includes the entire portion of the tooth covered by enamel, extending from the gumline to the tip of the crown. This technique restores not only the external shape but also the thickness and structure of the enamel and dentin, creating a result that closely resembles a natural tooth in both form and function.
Here are some notable advantages of anatomical porcelain crowns:
- Precise design: Anatomical porcelain crowns are crafted with highly accurate dimensions, natural curvature, and contours that closely match the proportions of real teeth. This precise design enhances the crown’s durability and improves its ability to withstand biting forces, resulting in a long-lasting and resilient restoration.
- Restoration effectiveness remains stable regardless of gum condition: According to experts, anatomical porcelain crowns are not influenced by gum issues such as recession or inflammation. These crowns are designed based on the fixed structure of the tooth, meaning their durability and shape remain stable regardless of the gum’s condition.
- High aesthetic value: Anatomical porcelain crowns fit snugly over the natural tooth stump, leaving no visible gaps. They create a smooth, natural-looking gumline, ensuring optimal aesthetic results and a seamless appearance with surrounding teeth.
- Chewing functionality: Anatomical porcelain crowns offer excellent strength and durability, with bite force evenly distributed across the tooth surface. This allows for smooth, efficient chewing and ensures long-term comfort during daily eating activities.
Anatomical crown is a modern dental technique aimed at maximizing the natural anatomical structure of real teeth. This method uses porcelain crowns that offer near-perfect compatibility with the tooth structure and surrounding gum tissue. It is widely praised by dental professionals for its precision, durability, and ability to closely replicate the look and function of natural teeth.
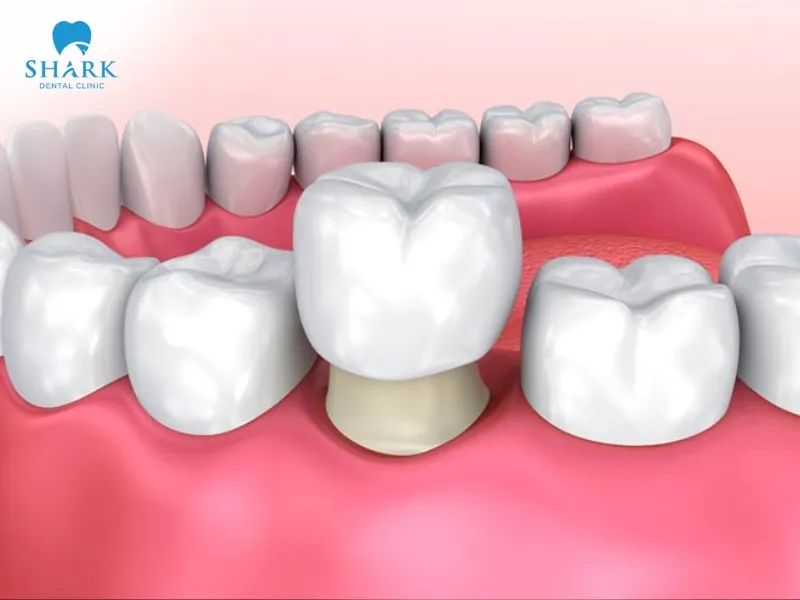
>>> See more: Can a crown get infected?
What is a clinical crown?
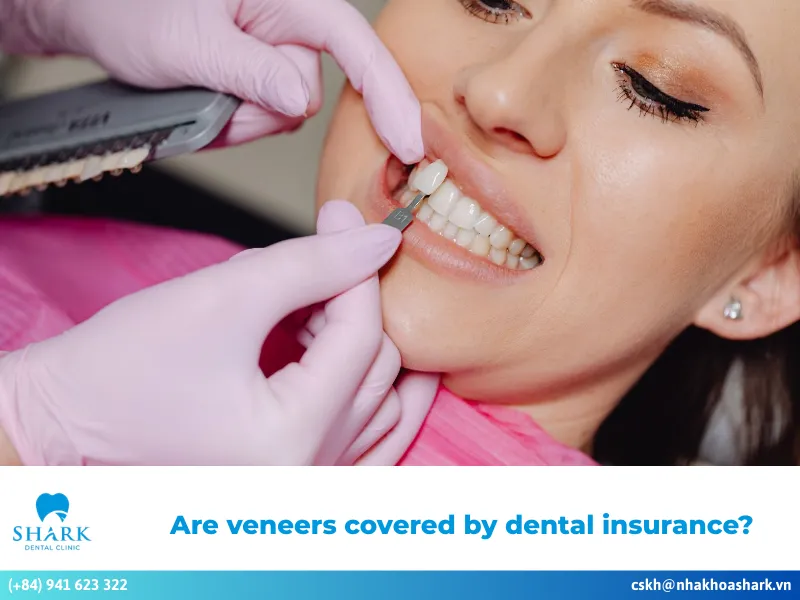
Clinical crown is a flexible dental restoration method that uses a porcelain crown crafted to cover only the portion of the tooth above the gumline. The crown is designed and fabricated based on the actual condition of the tooth inside the oral cavity, taking into account factors such as gum recession, periodontal disease, and tooth inflammation.
Here are some notable advantages of the clinical crown method:
- Flexible for each case: Clinical crown is suitable for various oral conditions. Specifically, in cases of gum recession, the porcelain crown is designed with greater coverage to fully conceal the exposed root surface, ensuring optimal restoration results without leaving gaps or visible margins.
- Adjustable crown design: The porcelain crown can be modified and crafted based on the natural tooth model and the “exposed area” of the tooth. It fits snugly over the tooth surface while also providing gum coverage tailored to the specific condition of each patient.
- Aesthetic Assurance: Clinical porcelain crowns are highly regarded for their aesthetic effectiveness, thanks to their natural size, color, curvature, and light-reflective properties that closely resemble real teeth. Additionally, these crowns are flexibly designed based on the tooth’s condition, helping to create a bright, even, and naturally beautiful smile.
The clinical crown method is recommended for cases where teeth are exposed due to periodontitis, gum recession, or uneven gum contours. Depending on the actual oral condition, the dentist will advise the most appropriate restoration approach tailored to each patient’s needs.
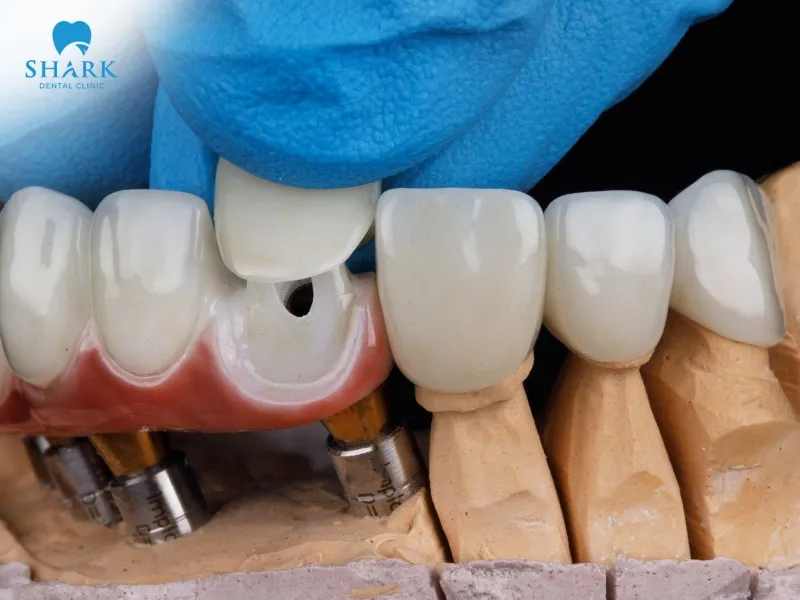
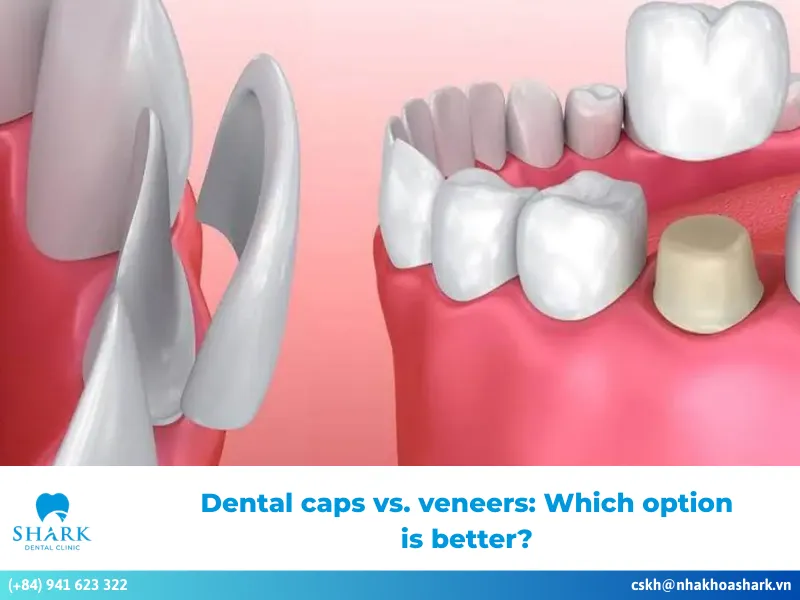
What is an anatomical crown and how is it different from a clinical crown?
Anatomical crown and clinical crown are two widely used methods in modern dentistry. Below is a detailed comparison table to help you better understand the differences between these two approaches:
| Criteria | Anatomical crown | Clinical crown |
| Shape | The shape of the anatomical crown is designed according to the tooth’s anatomical structure, including the enamel-covered part, extending from the gumline to the tip of the tooth. This shape is not affected by the actual condition of the gums. | The shape of the clinical crown is designed based on the part of the tooth exposed above the gums. This crown is adjusted in size and shape to match the actual condition, such as gum recession, gingivitis, or periodontitis, ensuring optimal and safe restoration results. |
| Size | The size of the anatomical crown is fixed, replicating the natural tooth from the gumline to the tip of the tooth. | The size of the clinical crown may vary depending on gum recession, inflammation, or soft tissue coverage. |
| Function | The anatomical crown method ensures high aesthetic results, superior durability, and a precise fit to the natural tooth, helping to fully restore the original tooth structure. | The clinical crown method focuses on restoring the visible part of the tooth, enhancing aesthetics along the current gumline, and adapting flexibly to each specific case. |
| Cost | The cost of anatomical crown is stable and less variable because it depends less on the actual oral condition. Currently, the cost ranges from approximately 1M to 14M VND per tooth. | The cost of clinical crown is higher and varies more depending on the condition of the gums. In some cases, gum surgery or soft tissue adjustments may be required, leading to higher costs. |
In summary, the anatomical crown method offers outstanding advantages in terms of stability and precision. It effectively recreates the natural tooth structure, ensuring both long-lasting durability and high aesthetic value. Anatomical porcelain crowns are designed to fit snugly over the natural tooth without affecting the surrounding tissues, providing maximum protection and shielding the tooth from external factors.
In contrast, clinical crown is highly valued for its flexibility. The porcelain crown is designed to focus on the visible portion of the tooth and can be adjusted based on specific conditions such as gum recession, periodontal disease, or soft tissue damage. However, because this method requires careful assessment and customization for each case, it involves more complex techniques and may come with a slightly higher cost.
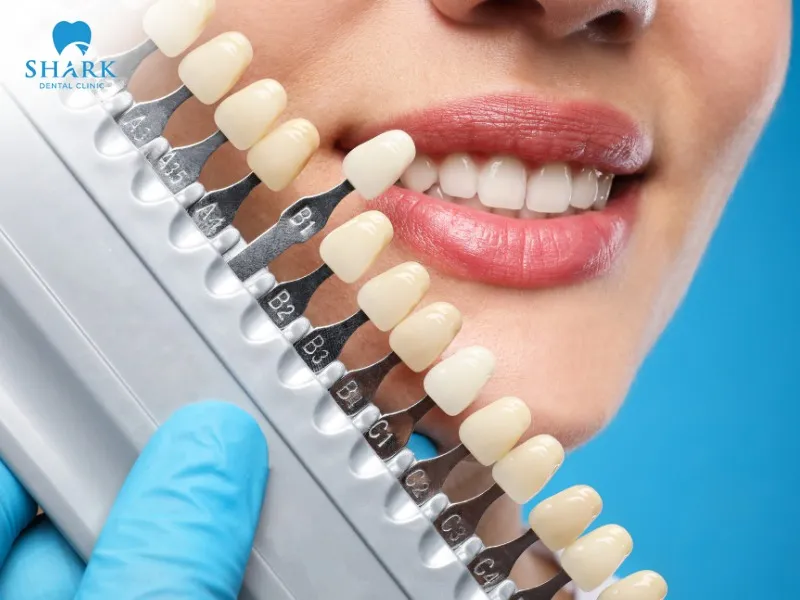
Therefore, choosing between anatomical crown and clinical crown should be based on the actual oral condition, the extent of gum tissue damage, the level of tooth exposure, aesthetic expectations, financial considerations, and other individual factors.
At reputable dental clinics, dentists will carefully examine your oral condition and recommend the most optimal solution to ensure both durability and aesthetics, tailored to each individual case.
The above article has provided comprehensive information on both anatomical crown and clinical crown methods. These insights help you clearly understand the differences between the two approaches, enabling you to choose a restoration solution that offers both long-lasting durability and aesthetic appeal. Wishing you a bright, even, and beautiful smile soon!
>>> See more: Alternatives to dental crowns