Dental X-ray imaging is considered one of the most essential diagnostic techniques, widely applied across modern dentistry. So, if you are looking for a guide on how to read a dental X-ray, follow the detailed explanation in the article below to get the answer that best supports your oral health decisions!
Why your dental X-Rays are so important?
Dental X-rays are a vital tool for capturing images inside the mouth, providing a clear view of the teeth, jawbone, tooth roots, and dental pulp. These images allow dentists to identify oral diseases, such as wisdom teeth problems and abscesses, enabling timely and effective treatment solutions.
Dental X-rays use X-ray beams that pass through the upper jaw area onto a film or digital sensor. The resulting images reveal the internal structures of the mouth, aiding dentists in diagnosing and treating various dental conditions.
Patients who are considering diagnostic imaging often also ask about dental X-ray cost in Vietnam before scheduling their examination.

Below are some key benefits of dental X-ray techniques:
- Identifying tooth morphology: Dental X-rays help accurately determine the shape of teeth and their movements, allowing dentists to address bite misalignment quickly and effectively.
- Early diagnosis: They enable early identification and evaluation of issues like gum inflammation, tooth decay, and pulpitis. This early detection allows dentists to recommend preventive measures to avoid serious complications.
- Safe tooth extractions: Dental X-rays provide insights into the details beneath tooth roots, including nerve canals and small blood vessels, ensuring safe extractions without risking bleeding or nerve damage.
- Assessing jawbone density: They facilitate accurate assessments of jawbone density, which is critical for various treatments.
- Detecting oral lesions: X-rays can help identify benign oral lesions, such as cysts or mild inflammation.
- Monitoring tooth eruption: For young children, dental X-rays assist in monitoring the eruption of permanent teeth.
- Overall oral health assessment: They provide comprehensive evaluations of oral health in cases involving porcelain crowns, braces, dental implants, and more.
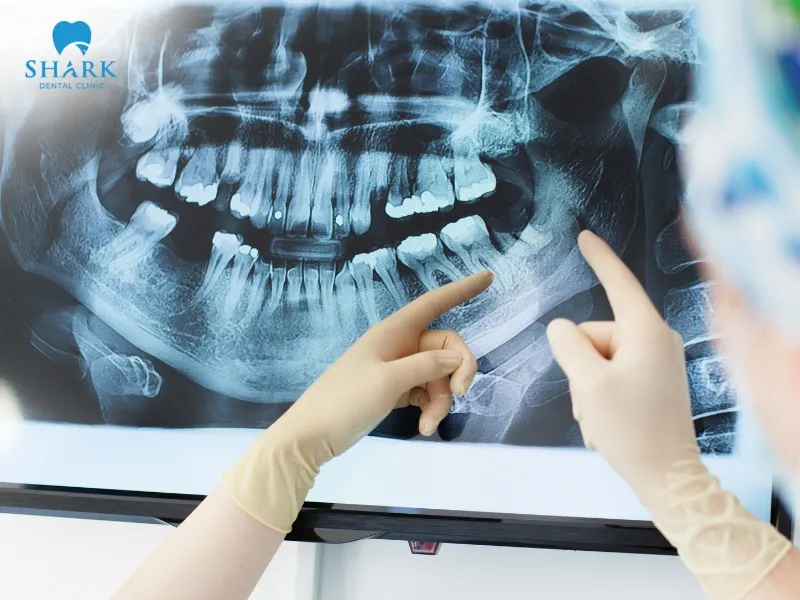
How to read a dental X-ray?
When examining a dental X-ray, you’ll notice areas in various shades, including white, gray, and black. These shades represent different structures in the teeth, bone, and soft tissues within your mouth. Understanding these color groups can help you interpret the X-ray and the dental conditions present.
Radiopaque — The bright and white stuff
Radiopaque regions appear as bright white sections on a dental X-ray. These areas indicate structures that are hard, thick, and highly resistant to X-rays, such as enamel and dentin, which are clear and noticeable.
- Enamel: The hardest tissue in the body, enamel is the brightest part of a dental X-ray.
- Dentin: Located beneath the enamel, dentin is also bright but not as prominent.
- Restorative materials: Common materials like fillings or metal crowns show up as very bright white areas on the X-ray.
- Jawbone: Denser parts of the jawbone also appear bright.
In general, bright areas on an X-ray indicate strong, dense dental structures. However, an unusually bright spot may suggest tooth misalignment, calcification, or the presence of foreign objects.
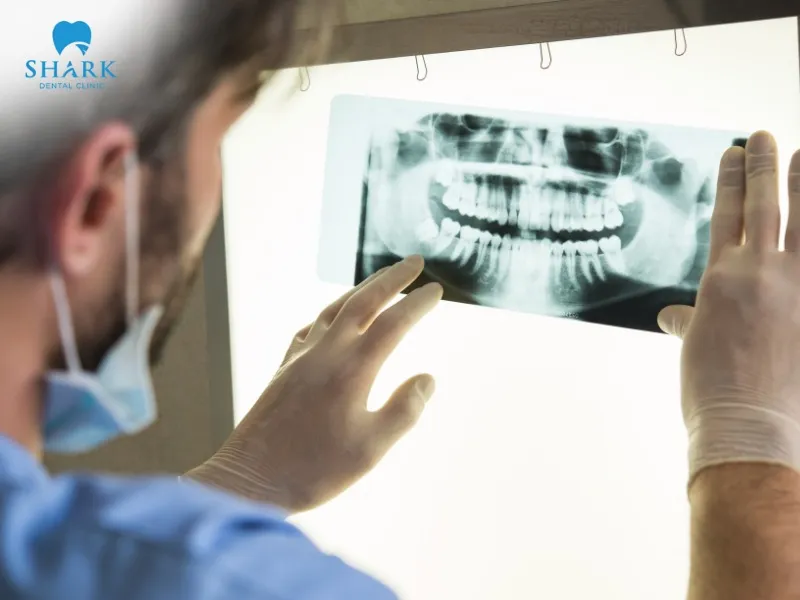
Radiolucent — The dark and gray areas
Radiolucent areas are the dark gray or black sections on a dental X-ray. These regions are where X-ray beams pass through easily; the softer or more hollow the structure, the darker it appears.
- Dental pulp: The pulp chamber at the center of the tooth contains soft tissue, appearing dark on the X-ray.
- Pathology: Other abnormal dark areas may include indications of tooth decay, periapical inflammation, bone loss, dental cysts, and more.
In some cases, dentists may also consider what does cancer look like on dental X-ray, as certain malignant lesions can present as irregular dark areas associated with progressive bone destruction.
A quick guide to X-Ray shades
- Bright, clear white: Bright and clear white areas on a dental X-ray represent hard structures that strongly block X-ray beams. These areas typically appear on enamel, dentin, or dental materials present in the oral cavity.
- Soft white, light gray: Regions that are soft white or light gray reflect moderately hard tooth structures, usually representing dentin beneath the enamel or areas of jawbone.
- Medium gray: Medium gray shades generally indicate soft tissues or hollow spaces inside the mouth, such as the periodontal ligament.
- Dark gray and black: Dark gray or black areas indicate where X-ray beams pass through easily, revealing hollow or soft regions. These commonly include the pulp chamber, tooth decay, and bone loss.
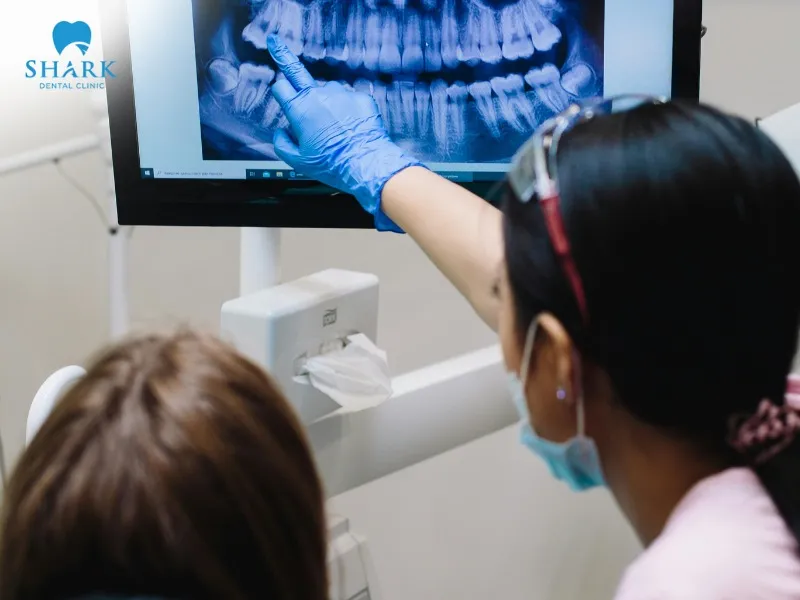
How to spot common dental issues on an X-ray
Dental X-ray techniques are widely used and frequently prescribed in dentistry. Through X-ray films, dentists can visualize tooth and bone structures, aiding in the early detection and diagnosis of common dental problems.
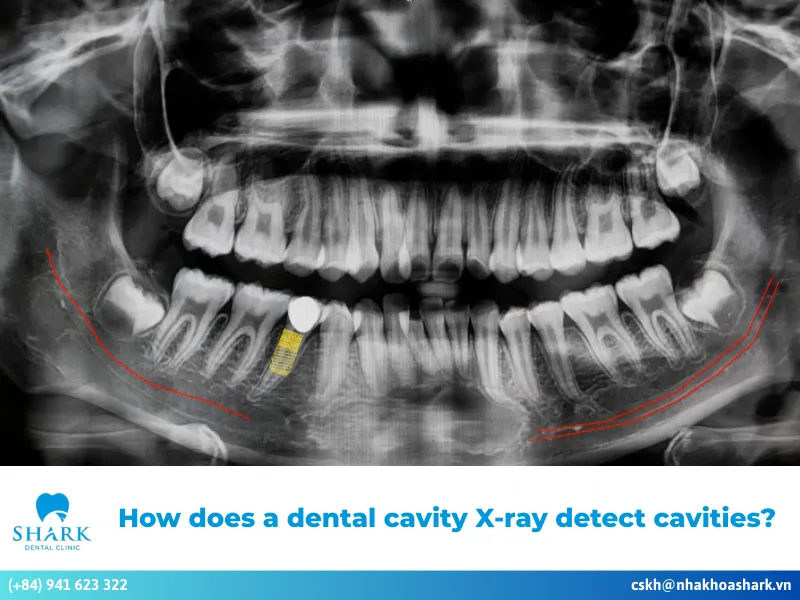
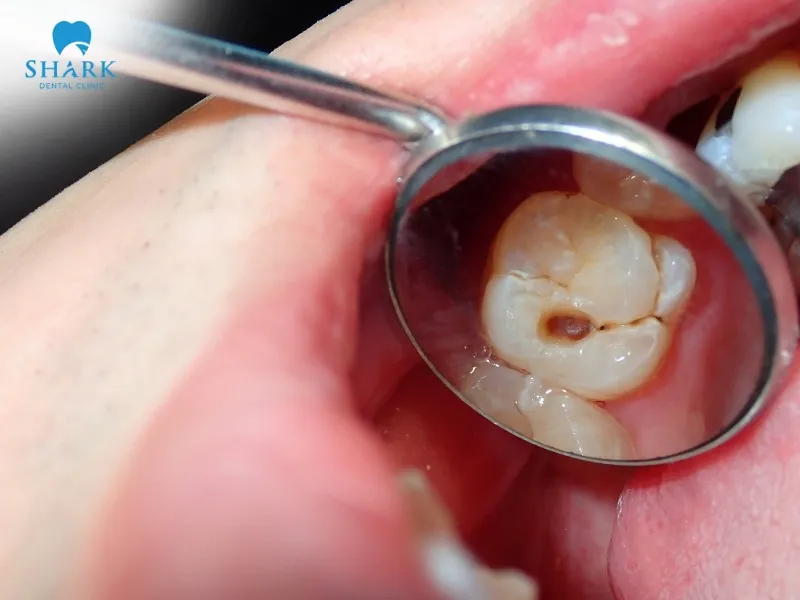
Finding cavities
Tooth decay caused by bacterial infection, which damages tooth structure, typically appears as dark areas on a dental X-ray. Cavities often show up on the tooth surface or between the teeth as small dark spots or patches of decay. Since decay destroys hard tooth structure, X-rays easily penetrate these weakened areas.
If cavities are located deep between teeth or beneath a filling where they can’t be seen with the naked eye, dentists can readily identify them on the X-ray as dark regions. Common indicators include irregularly shaped dark patches with blurred edges that extend toward the pulp chamber.
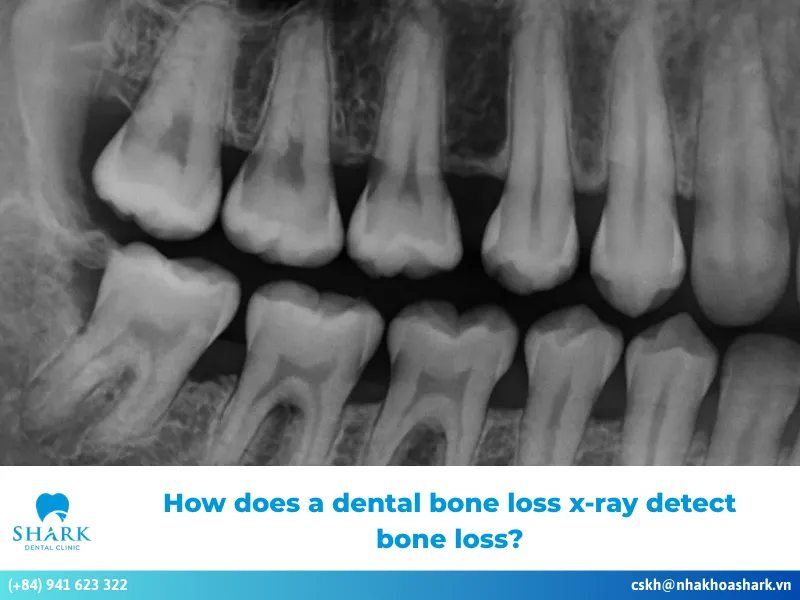
Identifying bone loss from gum disease
Bone loss caused by gum disease is also easily detected on a dental X-ray. Normally, the bone surrounding the teeth is level at the neck of the tooth, forming a smooth, even margin. When bone is resorbed or lost, this margin drops downward, creating a wider space between the tooth and the bone.
On a dental X-ray, dentists may observe an increased distance between the tooth and the bone, with a clearly visible dark region. The more bone loss there is, the larger the dark space becomes, and the lower the bone margin appears. This information helps dentists evaluate and predict the long-term condition of the tooth.
Spotting infections and abscesses
If large dark areas are visible on a dental X-ray, they may indicate infection or a dental abscess. When bacteria persist for an extended period and aggressively attack the tooth, they can destroy surrounding bone, leading to large hollow spaces that allow X-rays to pass through easily.
In many cases, a specialist will use an abscessed tooth infected root canal X-ray to pinpoint exactly where the infection has spread. On the X-ray, you may see an oval or round black area around the tooth roots, often accompanied by a blurred bone margin. At this stage, the tooth root or pulp is likely compromised, and an abscess has already formed, requiring immediate intervention.

This guide provides a thorough and understandable overview of how to read a dental X-ray. Dental X-rays are a common and essential diagnostic tool in dentistry, helping to identify various conditions so your dentist can determine the most effective treatment solutions. We hope this gives you a clearer understanding of how dental X-rays work!
>>> See more: What OSHA standard applies to all medical and dental offices that have X-ray machines?