Dental X-rays are a common dental technique that provides accurate diagnostic images, helping dentists diagnose oral health conditions effectively. However, one of the primary issues many people are concerned about is: are dental X-rays safe? This question will be clearly explained in the article below!
Are dental X-rays safe?
Dental X-rays are generally considered safe because the amount of radiation used in dental imaging is strictly controlled and remains within permitted limits, posing minimal risk to overall health.
The dental X-ray procedure is quick and performed in a controlled clinical environment with very low radiation intensity. The X-ray beam is precisely focused on the specific area being examined, and patients are provided with protective lead aprons to minimize whole-body exposure. These safeguards ensure that safety is not a major concern for most patients when it comes to dental X-rays.
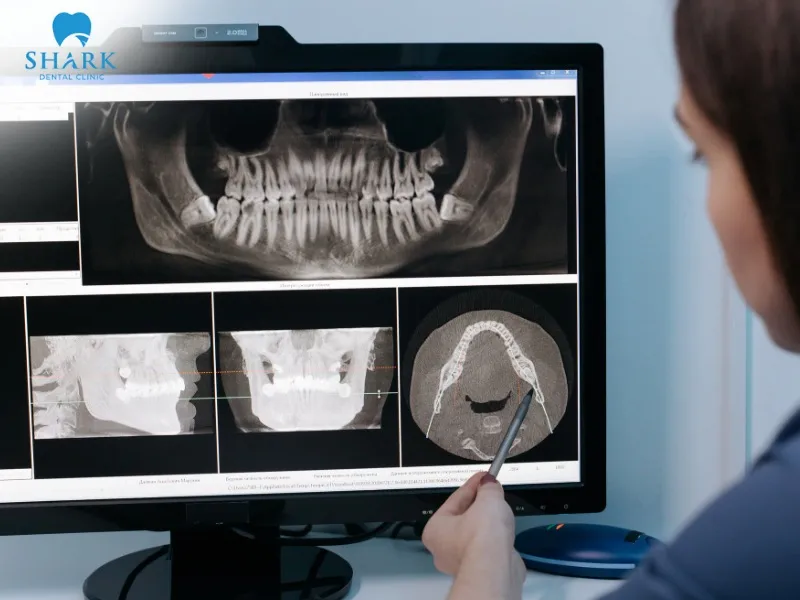
Understanding dental X-Ray radiation levels
While dental X-rays are tightly regulated and considered safe, radiation exposure and potential risks can still be a concern for some individuals. In reality, the health impact of radiation largely depends on the dose to which the body is exposed.
For dental X-rays, radiation levels can vary based on the type and location of the image taken. Generally, adults in good health can tolerate higher radiation levels compared to children. Therefore, dental X-rays for children should only be performed when clearly necessary and medically indicated.
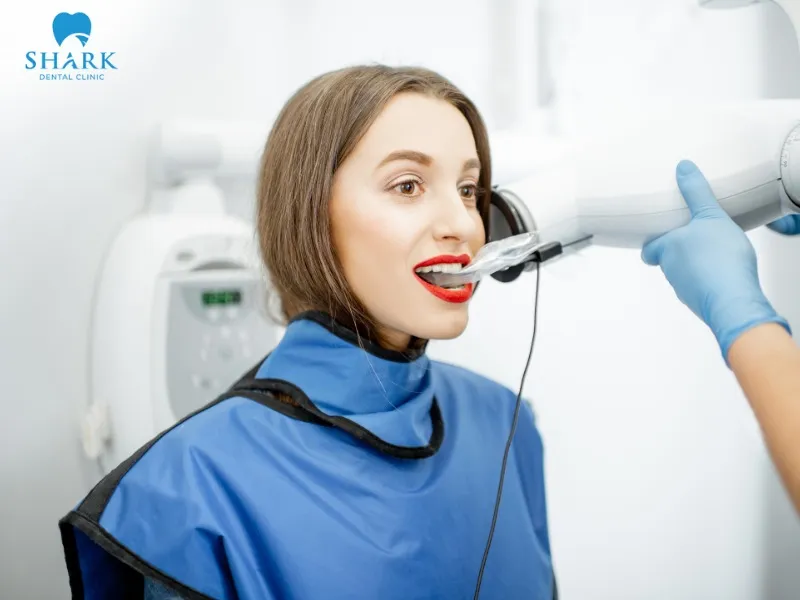

How much radiation in dental X-Rays?
Experts note that X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation that can affect cellular tissues. For this reason, dental X-rays must follow standardized protocols to keep radiation doses within safe limits.
The American Dental Association (ADA) states that the radiation dose from a single dental X-ray is very low, typically ranging from approximately 5 to 24 microsieverts (µSv) depending on the type of dental X-ray. This level of exposure is considered negligible and generally does not pose a health risk.
>>> See more: Can i refuse dental x rays?
Dental X-Rays vs. CBCT: Which has more radiation?
CT scans generally involve higher radiation levels than standard dental X-rays. However, Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) imaging is also carefully controlled to ensure that exposure remains within safe limits. CBCT provides highly detailed 3D images and is commonly used in procedures such as dental implant placement, root canal treatment, and etc.
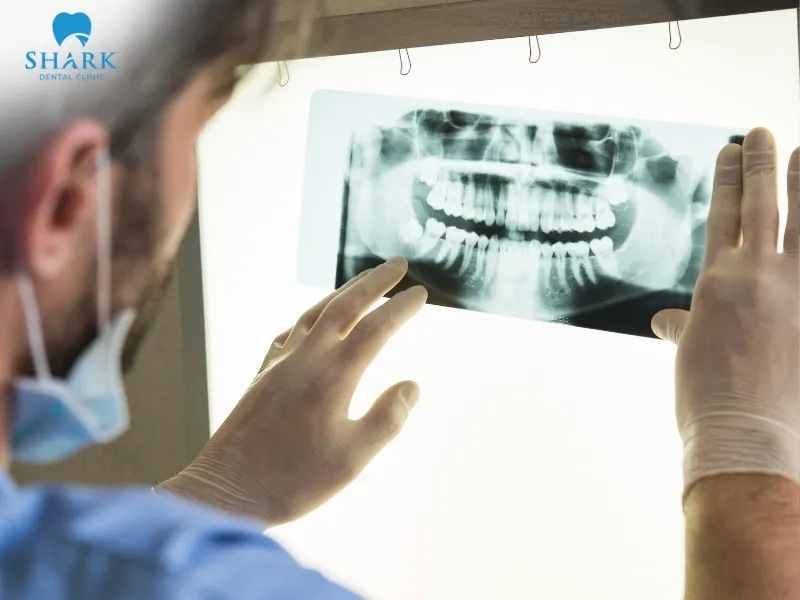
How dentists minimize radiation exposure (ALARA protocol)
There are several measures to reduce radiation exposure during dental X-ray imaging by following the ALARA principle:
- Use of lead aprons: Lead aprons shield sensitive areas like the neck, chest, and abdomen, helping to protect vital organs, such as the thyroid gland and reproductive organs, from unnecessary exposure.
- Limiting the number of X-rays: Dental X-rays are prescribed only when clinically necessary. Dentists carefully control the frequency of imaging to ensure maximum patient safety.
- Advanced technology: Modern dental X-ray systems allow for precise control of radiation doses while producing high-resolution images. This technology enables accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning with minimal exposure.
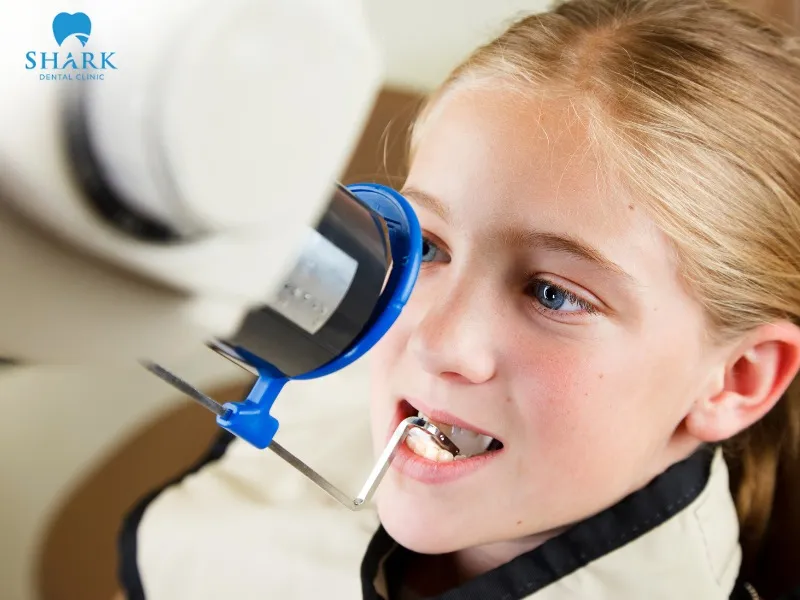
Safety guidelines for children
In certain necessary cases, children may require dental X-rays to assist in early diagnosis or orthodontic planning. To ensure safety, children must wear specialized lead protective equipment. This shielding helps disperse X-ray radiation and significantly reduces its impact on developing tissues.
In summary, the question “Are dental X-rays safe?” has been thoroughly addressed in this article. Dental X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and preventing oral health conditions. Hopefully, this information helps readers better understand dental X-rays and feel more confident and reassured when undergoing this important diagnostic procedure.
>>> See more: Dental X-ray in Ho Chi Minh